Stellar Classification
Astronomers began to categorise stars, based on their mass and temperature, hundreds of years ago. As scientists have learned more about stars, this classification scheme has had to evolve.
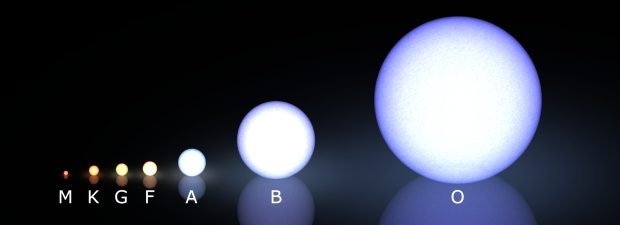
Stars are grouped into 7 main categories (also called, classes). These were created by astronomer Annie Jump Cannon. The classes are called O, B, A, F, G, K and M. Stars in the 'O' class are the most massive and hottest, stars in the 'M' class are the smallest and coolest.
Credit: Keiff/Wiki
If you look closely at stars in the sky, you notice they are not all the same colour. Some appear redder and some appear bluer. The colour of light a star gives off is controlled by its temperature. Hotter 'O' stars glow bluer and cooler 'M' stars glow redder. This is similar to what happens when you heat up metal to very high temperatures. As the metal heats up, it will start to glow red. As it gets hotter, that red becomes more yellow and then white. Eventually, the metal will be hot enough to glow a bright blue colour.
Our closest star, the Sun, shines with a yellow light. The Sun is classed as 'G' star, with a temperature of about 5,800 °K. (When talking about the temperature of stars, we usually use the unit 'Kelvin' - 5,800 °K is about 5,500 °C.)
The hotter stars are usually much less common than the cooler, redder ones. For example 'O' type stars make up only 1 in every 3 million stars we see. The next hottest, 'B' stars are more common, making up 1 in 800. Then each cooler subtype gets more and more common. The coolest 'M' type stars make up 75% of all of the stars we see.
We can be even more accurate when we categorise stars by splitting each class into 10 smaller sub-classes. These sub-classes are numbered 0 - 9, with 0 being hotter than 1. For example, the Sun is actually a G2 star. This is hotter than a G7 star, but cooler than a G0 star. Similarly, a B9 star is cooler than a B4 star.
The table on this page lists the temperature ranges and colours for each class of star.
| Class | Temperature (°K) | Colour | Example Star |
| O | 30,000 - 50,000 | Blue | Alnitak |
| B | 10 000 - 30,000 | Blue-White | Rigel |
| A | 7,500 - 10,000 | White | Vega |
| F | 6,000 - 7,500 | Yellow-White | Procyon |
| G | 5,200 - 6,000 | Yellow | The Sun |
| K | 3,700 - 5,200 | Orange | Pollux |
| M | < 3,700 | Red | Betelgeuse |

